The Company
Gas Strut Engineering Ltd have been manufacturing gas struts in Bedford for over 30 years. The company specialises in the design and production of gas struts to customer’s specifications on short lead times. We also hold large stocks of commonly used sizes which are available on a next day delivery. We pride ourselves on giving good service and technical assistance whenever required.

How a Gas Strut Works
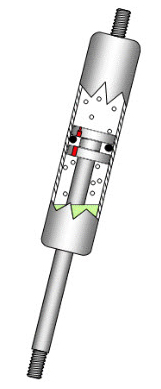
A gas strut comprises of a piston rod which slides in and out of a pressurised sealed tube. The rod has a piston attached to the end which has a small orifice in it. This allows gas pressure to equalise either side. As the gas strut extends, gas is forced through the small hole which controls the speed at which the gas strut extends. It also acts as a stop and prevents the rod from being forced out of the tube.
The force output of the gas strut is determined by the diameter of the piston rod and the pressure of the gas inside the cylinder. The larger the rod and higher the gas pressure, the higher the gas strut force
Inside the gas strut, as well as nitrogen gas, there is a small quantity of hydraulic fluid. This acts as a lubricant and as a hydraulic check at the end of the stroke.
The Characteristics of a Gas Strut
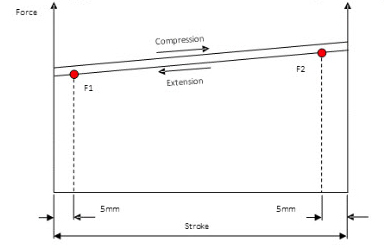
Figure 1 below shows how the force of a gas strut increases as it compresses. The force increase is linear and is much less than most other types of spring.
By convention, gas strut force is measured 5mm before full extension in the extension direction (F1). The compressed force is sometimes important and this is measured 5mm after full compression in the extension direction (F2)
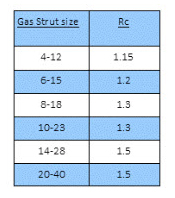
The force increase can be expressed as a ratio Rc, where Rc = F1/F2
By altering the stroke length, rod and tube diameter and the quantity of hydraulic fluid, the spring rate can be varied to suit the application.
The force increase can be expressed as a ratio Rc, where Rc = F1/F2
By altering the stroke length, rod and tube diameter and the quantity of hydraulic fluid, the spring rate can be varied to suit the application.